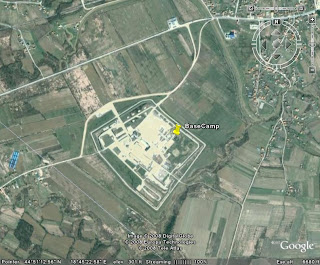
This is the view of the base camp I was stationed at in Bosnia-Herzegovina from 2001-02, Camp McGovern. It lies on the outskirts of the town of Brcko, the district seat. The reason the details have been distorted is to maintain operational security; the bad guys can utilize this tool just as easily as the good guys. The remote sensing data displayed here is aerial photography. I believe that it is an infrared emulsion, the same type that the USGS uses to produce DOQQ's. I say this because with a DOQQ, true distance can be measured due to corrections in camera angle & relief; true distance can be measured in this image, as well.

